#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
r"""
Two-dimensional variable-coefficient acoustics on a mapped grid
===============================================================
Solve the variable-coefficient acoustics equations in 2D:
.. math::
p_t + K(x,y) (u_x + v_y) & = 0 \\
u_t + p_x / \rho(x,y) & = 0 \\
v_t + p_y / \rho(x,y) & = 0.
Here p is the pressure, (u,v) is the velocity, :math:`K(x,y)` is the bulk modulus,
and :math:`\rho(x,y)` is the density.
This example shows how to solve a problem with variable coefficients on a mapped grid.
The domain contains circular inclusions with different acoustic properties.
"""
import numpy as np
# Circle radius, square radius, circle center:
# ((r1, r2), (x0, y0))
circles = ( ((0.15,0.204),( 0.45,0.3)),
((0.15,0.204),( 0.7, 0.75)))
impedance = (12.,10.)
sound_speed = (0.3,1.5)
def inclusion_mapping(xc, yc):
"""Apply mapping from square to circle for each circle specified.
Leave rest of grid cartesian.
"""
xp = xc+0.
yp = yc+0.
for circle in circles:
circle_center = circle[1]
r1 = circle[0][0]
r2 = circle[0][1]
x0, y0 = circle_center
xdist = np.abs(xc-x0)
ydist = np.abs(yc-y0)
insquare = np.where(np.maximum(xdist,ydist)<=r2) # Square section of grid to be deformed
xc0 = (xc[insquare]-x0)/r2
yc0 = (yc[insquare]-y0)/r2
xc1 = np.abs(xc0)
yc1 = np.abs(yc0)
d = np.maximum(xc1, yc1)
d = np.maximum(d,1.e-10)
d = np.minimum(d, 0.99999)
d1 = d*r2/np.sqrt(2)
# Pick mapping
#R = np.sqrt(2) * d1
R = r1*np.ones(d1.shape)
R = r1**2 / (r2*d)
# Modify d1 and R outside circle to morph back to square:
ij = np.where(d>(r1/r2))
d1[ij] = r1/np.sqrt(2) + (d[ij]-r1/r2)*(r2-r1/np.sqrt(2))/(1.-r1/r2)
R[ij] = r1 * ((1.-r1/r2) / (1.-d[ij]))**(r2/r1 + 0.5)
xp2 = d1/d * xc1
yp2 = d1/d * yc1
center = d1 - np.sqrt(R**2 - d1**2)
ij = np.where(xc1>=yc1)
xp2[ij] = center[ij] + np.sqrt(R[ij]**2 - yp2[ij]**2)
ij = np.where(yc1>=xc1)
yp2[ij] = center[ij] + np.sqrt(R[ij]**2 - xp2[ij]**2)
xp2 = np.sign(xc0) * xp2
yp2 = np.sign(yc0) * yp2
xp[insquare] = x0 + xp2
yp[insquare] = y0 + yp2
return xp, yp
def compute_geometry(grid):
r"""Computes
a_x
a_y
length_ratio_left
b_x
b_y
length_ratio_bottom
cell_area
"""
dx, dy = grid.delta
area_min = 1.e6
area_max = 0.0
x_corners, y_corners = grid.p_nodes
lower_left_y, lower_left_x = y_corners[:-1,:-1], x_corners[:-1,:-1]
upper_left_y, upper_left_x = y_corners[:-1,1: ], x_corners[:-1,1: ]
lower_right_y, lower_right_x = y_corners[1:,:-1], x_corners[1:,:-1]
upper_right_y, upper_right_x = y_corners[1:,1: ], x_corners[1:,1: ]
a_x = upper_left_y - lower_left_y #upper left and lower left
a_y = -(upper_left_x - lower_left_x)
anorm = np.sqrt(a_x**2 + a_y**2)
a_x, a_y = a_x/anorm, a_y/anorm
length_ratio_left = anorm/dy
b_x = -(lower_right_y - lower_left_y) #lower right and lower left
b_y = lower_right_x - lower_left_x
bnorm = np.sqrt(b_x**2 + b_y**2)
b_x, b_y = b_x/bnorm, b_y/bnorm
length_ratio_bottom = bnorm/dx
area = 0*grid.c_centers[0]
area += 0.5 * (lower_left_y+upper_left_y)*(upper_left_x-lower_left_x)
area += 0.5 * (upper_left_y+upper_right_y)*(upper_right_x-upper_left_x)
area += 0.5 * (upper_right_y+lower_right_y)*(lower_right_x-upper_right_x)
area += 0.5 * (lower_right_y+lower_left_y)*(lower_left_x-lower_right_x)
area = area/(dx*dy)
area_min = min(area_min, np.min(area))
area_max = max(area_max, np.max(area))
return a_x, a_y, length_ratio_left, b_x, b_y, length_ratio_bottom, area
def incoming_square_wave(state,dim,t,qbc,auxbc,num_ghost):
"""
Incoming square wave at left boundary.
"""
if t<0.05:
s = 1.0
else:
s = 0.0
for i in range(num_ghost):
reflect_ind = 2*num_ghost - i - 1
alpha = auxbc[0,i,:]
beta = auxbc[1,i,:]
u_normal = alpha*qbc[1,reflect_ind,:] + beta*qbc[2,reflect_ind,:]
u_tangential = -beta*qbc[1,reflect_ind,:] + alpha*qbc[2,reflect_ind,:]
u_normal = 2.0*s - u_normal
qbc[0,i,:] = qbc[0,reflect_ind,:]
qbc[1,i,:] = alpha*u_normal - beta*u_tangential
qbc[2,i,:] = beta*u_normal + alpha*u_tangential
def setup(kernel_language='Fortran', use_petsc=False, outdir='./_output',
solver_type='classic', time_integrator='SSP104', lim_type=2,
num_output_times=20, disable_output=False, num_cells=200):
from clawpack import riemann
if use_petsc:
import clawpack.petclaw as pyclaw
else:
from clawpack import pyclaw
riemann_solver = riemann.acoustics_mapped_2D
if solver_type=='classic':
solver=pyclaw.ClawSolver2D(riemann_solver)
solver.dimensional_split=False
solver.limiters = pyclaw.limiters.tvd.MC
elif solver_type=='sharpclaw':
solver=pyclaw.SharpClawSolver2D(riemann_solver)
solver.time_integrator=time_integrator
solver.bc_lower[0]=pyclaw.BC.custom
solver.user_bc_lower = incoming_square_wave
solver.bc_upper[0]=pyclaw.BC.extrap
solver.bc_lower[1]=pyclaw.BC.extrap
solver.bc_upper[1]=pyclaw.BC.extrap
solver.aux_bc_lower[0]=pyclaw.BC.extrap
solver.aux_bc_upper[0]=pyclaw.BC.extrap
solver.aux_bc_lower[1]=pyclaw.BC.extrap
solver.aux_bc_upper[1]=pyclaw.BC.extrap
x = pyclaw.Dimension(0.,1.0,num_cells,name='x')
y = pyclaw.Dimension(0.,1.0,num_cells,name='y')
domain = pyclaw.Domain([x,y])
num_eqn = 3
num_aux = 9 # geometry (7), impedance, sound speed
state = pyclaw.State(domain,num_eqn,num_aux)
state.grid.mapc2p = inclusion_mapping
a_x, a_y, length_left, b_x, b_y, length_bottom, area = compute_geometry(state.grid)
state.aux[0,:,:] = a_x
state.aux[1,:,:] = a_y
state.aux[2,:,:] = length_left
state.aux[3,:,:] = b_x
state.aux[4,:,:] = b_y
state.aux[5,:,:] = length_bottom
state.aux[6,:,:] = area
state.index_capa = 6 # aux[6,:,:] holds the capacity function
grid = state.grid
xp, yp = grid.p_centers
state.aux[7,:,:] = 1.0 # Impedance
state.aux[8,:,:] = 1.0 # Sound speed
for i, circle in enumerate(circles):
# Set impedance and sound speed in each inclusion
radius = circle[0][0]
x0, y0 = circle[1]
distance = np.sqrt( (xp-x0)**2 + (yp-y0)**2 )
in_circle = np.where(distance <= radius)
state.aux[7][in_circle] = impedance[i]
state.aux[8][in_circle] = sound_speed[i]
# Set initial condition
state.q[0,:,:] = 0.
state.q[1,:,:] = 0.
state.q[2,:,:] = 0.
claw = pyclaw.Controller()
claw.keep_copy = True
if disable_output:
claw.output_format = None
claw.solution = pyclaw.Solution(state,domain)
claw.solver = solver
claw.outdir = outdir
claw.tfinal = 0.9
claw.num_output_times = num_output_times
claw.write_aux_init = True
claw.setplot = setplot
if use_petsc:
claw.output_options = {'format':'binary'}
return claw
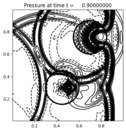
def setplot(plotdata):
"""
Plot solution using VisClaw.
This example shows how to mark an internal boundary on a 2D plot.
"""
from clawpack.visclaw import colormaps
plotdata.clearfigures() # clear any old figures,axes,items data
plotdata.mapc2p = inclusion_mapping
# Figure for pressure
plotfigure = plotdata.new_plotfigure(name='Pressure', figno=0)
# Set up for axes in this figure:
plotaxes = plotfigure.new_plotaxes()
plotaxes.title = 'Pressure'
plotaxes.scaled = True # so aspect ratio is 1
plotaxes.afteraxes = plot_circles
# Set up for item on these axes:
plotitem = plotaxes.new_plotitem(plot_type='2d_contour')
plotitem.contour_nlevels = 100
plotitem.contour_min = -2.51
plotitem.contour_max = 2.51
plotitem.plot_var = 0
# Figure for x-velocity plot
plotfigure = plotdata.new_plotfigure(name='x-Velocity', figno=1)
# Set up for axes in this figure:
plotaxes = plotfigure.new_plotaxes()
plotaxes.title = 'u'
plotaxes.afteraxes = plot_circles
plotitem = plotaxes.new_plotitem(plot_type='2d_pcolor')
plotitem.plot_var = 1
plotitem.pcolor_cmap = 'RdBu'
plotitem.add_colorbar = True
plotitem.pcolor_cmin = -1.0
plotitem.pcolor_cmax= 1.0
return plotdata
def plot_circles(current_data):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ax = plt.gca()
for circle in circles:
x0, y0 = circle[1]
radius = circle[0][0]
circle1=plt.Circle((x0,y0),radius,color='k',fill=False,lw=3)
ax.add_artist(circle1)
if __name__=="__main__":
import sys
from clawpack.pyclaw.util import run_app_from_main
output = run_app_from_main(setup,setplot)