2-dimensional variable-coefficient advection¶
Advection in an annular domain¶
Solve the linear non-conservative advection equation:
\[q_t + u(x,y) q_x + v(x,y) q_y = 0\]
in an annular domain, using a mapped grid.
Here q is the density of some quantity and (u,v) is the velocity field. We take a rotational velocity field: \(u = \cos(\theta), v = \sin(\theta)\).
This is the simplest example that shows how to use a mapped grid in PyClaw. However, it doesn’t use a mapped-grid Riemann solver.
Output:¶
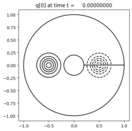
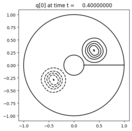

Source:¶
#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
r"""
Advection in an annular domain
==============================
Solve the linear non-conservative advection equation:
.. math::
q_t + u(x,y) q_x + v(x,y) q_y = 0
in an annular domain, using a mapped grid.
Here q is the density of some quantity and (u,v) is the velocity
field. We take a rotational velocity field: :math:`u = \cos(\theta), v = \sin(\theta)`.
This is the simplest example that shows how to use a mapped grid in PyClaw.
However, it doesn't use a mapped-grid Riemann solver.
"""
import numpy as np
def mapc2p_annulus(xc, yc):
"""
Specifies the mapping to curvilinear coordinates.
Inputs: c_centers = Computational cell centers
[array ([Xc1, Xc2, ...]), array([Yc1, Yc2, ...])]
Output: p_centers = Physical cell centers
[array ([Xp1, Xp2, ...]), array([Yp1, Yp2, ...])]
"""
p_centers = []
# Polar coordinates (first coordinate = radius, second coordinate = theta)
p_centers.append(xc[:]*np.cos(yc[:]))
p_centers.append(xc[:]*np.sin(yc[:]))
return p_centers
def qinit(state):
"""
Initialize with two Gaussian pulses.
"""
# First gaussian pulse
A1 = 1. # Amplitude
beta1 = 40. # Decay factor
r1 = -0.5 # r-coordinate of the center
theta1 = 0. # theta-coordinate of the center
# Second gaussian pulse
A2 = -1. # Amplitude
beta2 = 40. # Decay factor
r2 = 0.5 # r-coordinate of the centers
theta2 = 0. # theta-coordinate of the centers
R, Theta = state.grid.p_centers
state.q[0,:,:] = A1*np.exp(-beta1*(np.square(R-r1) + np.square(Theta-theta1)))\
+ A2*np.exp(-beta2*(np.square(R-r2) + np.square(Theta-theta2)))
def ghost_velocities_upper(state,dim,t,qbc,auxbc,num_ghost):
"""
Set the velocities for the ghost cells outside the outer radius of the annulus.
In the computational domain, these are the cells at the top of the grid.
"""
grid=state.grid
if dim == grid.dimensions[0]:
dx, dy = grid.delta
R_nodes,Theta_nodes = grid.p_nodes_with_ghost(num_ghost=2)
auxbc[:,-num_ghost:,:] = edge_velocities_and_area(R_nodes[-num_ghost-1:,:],Theta_nodes[-num_ghost-1:,:],dx,dy)
else:
raise Exception('Custom BC for this boundary is not appropriate!')
def ghost_velocities_lower(state,dim,t,qbc,auxbc,num_ghost):
"""
Set the velocities for the ghost cells outside the inner radius of the annulus.
In the computational domain, these are the cells at the bottom of the grid.
"""
grid=state.grid
if dim == grid.dimensions[0]:
dx, dy = grid.delta
R_nodes,Theta_nodes = grid.p_nodes_with_ghost(num_ghost=2)
auxbc[:,0:num_ghost,:] = edge_velocities_and_area(R_nodes[0:num_ghost+1,:],Theta_nodes[0:num_ghost+1,:],dx,dy)
else:
raise Exception('Custom BC for this boundary is not appropriate!')
def edge_velocities_and_area(R_nodes,Theta_nodes,dx,dy):
"""This routine fills in the aux arrays for the problem:
aux[0,i,j] = u-velocity at left edge of cell (i,j)
aux[1,i,j] = v-velocity at bottom edge of cell (i,j)
aux[2,i,j] = physical area of cell (i,j) (relative to area of computational cell)
"""
mx = R_nodes.shape[0]-1
my = R_nodes.shape[1]-1
aux = np.empty((3,mx,my), order='F')
# Bottom-left corners
Xp0 = R_nodes[:mx,:my]
Yp0 = Theta_nodes[:mx,:my]
# Top-left corners
Xp1 = R_nodes[:mx,1:]
Yp1 = Theta_nodes[:mx,1:]
# Top-right corners
Xp2 = R_nodes[1:,1:]
Yp2 = Theta_nodes[1:,1:]
# Top-left corners
Xp3 = R_nodes[1:,:my]
Yp3 = Theta_nodes[1:,:my]
# Compute velocity component
aux[0,:mx,:my] = (stream(Xp1,Yp1)- stream(Xp0,Yp0))/dy
aux[1,:mx,:my] = -(stream(Xp3,Yp3)- stream(Xp0,Yp0))/dx
# Compute area of the physical element
area = 1./2.*( (Yp0+Yp1)*(Xp1-Xp0) +
(Yp1+Yp2)*(Xp2-Xp1) +
(Yp2+Yp3)*(Xp3-Xp2) +
(Yp3+Yp0)*(Xp0-Xp3) )
# Compute capa
aux[2,:mx,:my] = area/(dx*dy)
return aux
def stream(Xp,Yp):
"""
Calculates the stream function in physical space.
Clockwise rotation. One full rotation corresponds to 1 (second).
"""
return np.pi*(Xp**2 + Yp**2)
def setup(use_petsc=False,outdir='./_output',solver_type='classic'):
from clawpack import riemann
if use_petsc:
import clawpack.petclaw as pyclaw
else:
from clawpack import pyclaw
if solver_type == 'classic':
solver = pyclaw.ClawSolver2D(riemann.vc_advection_2D)
solver.dimensional_split = False
solver.transverse_waves = 2
solver.order = 2
elif solver_type == 'sharpclaw':
solver = pyclaw.SharpClawSolver2D(riemann.vc_advection_2D)
solver.bc_lower[0] = pyclaw.BC.extrap
solver.bc_upper[0] = pyclaw.BC.extrap
solver.bc_lower[1] = pyclaw.BC.periodic
solver.bc_upper[1] = pyclaw.BC.periodic
solver.aux_bc_lower[0] = pyclaw.BC.custom
solver.aux_bc_upper[0] = pyclaw.BC.custom
solver.user_aux_bc_lower = ghost_velocities_lower
solver.user_aux_bc_upper = ghost_velocities_upper
solver.aux_bc_lower[1] = pyclaw.BC.periodic
solver.aux_bc_upper[1] = pyclaw.BC.periodic
solver.dt_initial = 0.1
solver.cfl_max = 0.5
solver.cfl_desired = 0.4
solver.limiters = pyclaw.limiters.tvd.vanleer
r_lower = 0.2
r_upper = 1.0
m_r = 40
theta_lower = 0.0
theta_upper = np.pi*2.0
m_theta = 120
r = pyclaw.Dimension(r_lower,r_upper,m_r,name='r')
theta = pyclaw.Dimension(theta_lower,theta_upper,m_theta,name='theta')
domain = pyclaw.Domain([r,theta])
domain.grid.mapc2p = mapc2p_annulus
domain.grid.num_ghost = solver.num_ghost
num_eqn = 1
state = pyclaw.State(domain,num_eqn)
qinit(state)
dx, dy = state.grid.delta
p_corners = state.grid.p_nodes
state.aux = edge_velocities_and_area(p_corners[0],p_corners[1],dx,dy)
state.index_capa = 2 # aux[2,:,:] holds the capacity function
claw = pyclaw.Controller()
claw.tfinal = 1.0
claw.solution = pyclaw.Solution(state,domain)
claw.solver = solver
claw.outdir = outdir
claw.setplot = setplot
claw.keep_copy = True
return claw
def setplot(plotdata):
"""
Plot solution using VisClaw.
"""
from clawpack.pyclaw.examples.advection_2d_annulus.mapc2p import mapc2p
import numpy as np
from clawpack.visclaw import colormaps
plotdata.clearfigures() # clear any old figures,axes,items data
plotdata.mapc2p = mapc2p
# Figure for contour plot
plotfigure = plotdata.new_plotfigure(name='contour', figno=0)
# Set up for axes in this figure:
plotaxes = plotfigure.new_plotaxes()
plotaxes.xlimits = 'auto'
plotaxes.ylimits = 'auto'
plotaxes.title = 'q[0]'
plotaxes.scaled = True
# Set up for item on these axes:
plotitem = plotaxes.new_plotitem(plot_type='2d_contour')
plotitem.plot_var = 0
plotitem.contour_levels = np.linspace(-0.9, 0.9, 10)
plotitem.contour_colors = 'k'
plotitem.patchedges_show = 1
plotitem.MappedGrid = True
# Figure for pcolor plot
plotfigure = plotdata.new_plotfigure(name='q[0]', figno=1)
# Set up for axes in this figure:
plotaxes = plotfigure.new_plotaxes()
plotaxes.xlimits = 'auto'
plotaxes.ylimits = 'auto'
plotaxes.title = 'q[0]'
plotaxes.scaled = True
# Set up for item on these axes:
plotitem = plotaxes.new_plotitem(plot_type='2d_pcolor')
plotitem.plot_var = 0
plotitem.pcolor_cmap = colormaps.red_yellow_blue
plotitem.pcolor_cmin = -1.
plotitem.pcolor_cmax = 1.
plotitem.add_colorbar = True
plotitem.MappedGrid = True
return plotdata
if __name__=="__main__":
from clawpack.pyclaw.util import run_app_from_main
output = run_app_from_main(setup,setplot)
