1-dimensional Euler equations¶
Shock-tube problem¶
Solve the one-dimensional Euler equations for inviscid, compressible flow:
\[\begin{split}\rho_t + (\rho u)_x & = 0 \\
(\rho u)_t + (\rho u^2 + p)_x & = 0 \\
E_t + (u (E + p) )_x & = 0.\end{split}\]
The fluid is an ideal gas, with pressure given by \(p=\rho (\gamma-1)e\) where e is internal energy.
This script runs a shock-tube problem.
Output:¶
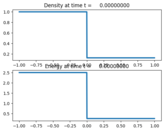
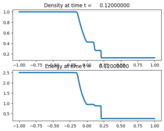
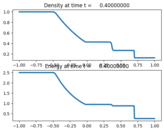
Source:¶
#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
r"""
Shock-tube problem
===================================
Solve the one-dimensional Euler equations for inviscid, compressible flow:
.. math::
\rho_t + (\rho u)_x & = 0 \\
(\rho u)_t + (\rho u^2 + p)_x & = 0 \\
E_t + (u (E + p) )_x & = 0.
The fluid is an ideal gas, with pressure given by :math:`p=\rho (\gamma-1)e` where
e is internal energy.
This script runs a shock-tube problem.
"""
from clawpack import riemann
from clawpack.riemann.euler_with_efix_1D_constants import density, momentum, energy, num_eqn
gamma = 1.4 # Ratio of specific heats
def setup(use_petsc=False, outdir='./_output', solver_type='classic',
kernel_language='Python',disable_output=False):
if use_petsc:
import clawpack.petclaw as pyclaw
else:
from clawpack import pyclaw
if kernel_language =='Python':
rs = riemann.euler_1D_py.euler_hllc_1D
elif kernel_language =='Fortran':
rs = riemann.euler_hlle_1D
if solver_type=='sharpclaw':
solver = pyclaw.SharpClawSolver1D(rs)
elif solver_type=='classic':
solver = pyclaw.ClawSolver1D(rs)
solver.kernel_language = kernel_language
solver.bc_lower[0]=pyclaw.BC.extrap
solver.bc_upper[0]=pyclaw.BC.extrap
mx = 800
x = pyclaw.Dimension(-1.0,1.0,mx,name='x')
domain = pyclaw.Domain([x])
state = pyclaw.State(domain,num_eqn)
state.problem_data['gamma'] = gamma
state.problem_data['gamma1'] = gamma - 1.
x = state.grid.x.centers
rho_l = 1.; rho_r = 1./8
p_l = 1.; p_r = 0.1
state.q[density ,:] = (x<0.)*rho_l + (x>=0.)*rho_r
state.q[momentum,:] = 0.
velocity = state.q[momentum,:]/state.q[density,:]
pressure = (x<0.)*p_l + (x>=0.)*p_r
state.q[energy ,:] = pressure/(gamma - 1.) + 0.5 * state.q[density,:] * velocity**2
claw = pyclaw.Controller()
claw.tfinal = 0.4
claw.solution = pyclaw.Solution(state,domain)
claw.solver = solver
claw.num_output_times = 10
claw.outdir = outdir
claw.setplot = setplot
claw.keep_copy = True
if disable_output:
claw.output_format = None
return claw
#--------------------------
def setplot(plotdata):
#--------------------------
"""
Specify what is to be plotted at each frame.
Input: plotdata, an instance of visclaw.data.ClawPlotData.
Output: a modified version of plotdata.
"""
plotdata.clearfigures() # clear any old figures,axes,items data
plotfigure = plotdata.new_plotfigure(name='', figno=0)
plotaxes = plotfigure.new_plotaxes()
plotaxes.axescmd = 'subplot(211)'
plotaxes.title = 'Density'
plotitem = plotaxes.new_plotitem(plot_type='1d')
plotitem.plot_var = density
plotitem.kwargs = {'linewidth':3}
plotaxes = plotfigure.new_plotaxes()
plotaxes.axescmd = 'subplot(212)'
plotaxes.title = 'Energy'
plotitem = plotaxes.new_plotitem(plot_type='1d')
plotitem.plot_var = energy
plotitem.kwargs = {'linewidth':3}
return plotdata
if __name__=="__main__":
from clawpack.pyclaw.util import run_app_from_main
output = run_app_from_main(setup,setplot)
